Swiss motorcycle license: categories, costs and requirements
Riding a motorcycle is attractive, but there is a somewhat complicated route to follow before getting there: which license category is the right one? Which courses do I need in Switzerland for the motorbike test? And how much does it all cost? Here's an overview of the most important information.
Do you dream of owning a motorbike? Then you're not alone. Young people in particular often toy with the idea of freedom and independence of owning their own motorcycle. For others, motorcycling is the perfect hobby: simply start it up, enjoy the power and effortlessness, a feeling almost like flying. But whether it's an electric scooter or a Harley, something for daily use or a passion, they all need a motorbike license. The type of license depends on the type of motorcycle you'd like to ride.
Motorcycles: what license categories are there?
There are three important criteria for dividing motorcycles into the various categories and sub-categories: engine size, power output and – for small motorcycles that can be ridden from age 15 – maximum speed.
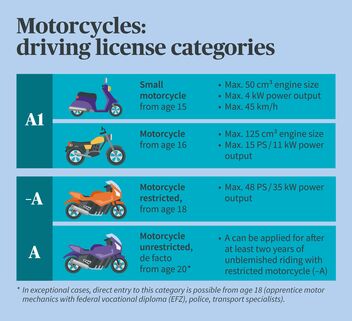
Incidentally, the previous A2 category no longer exists. It was withdrawn to match EU law and integrated into B1 (small and three-wheeled motor vehicles with an empty weight of max. 550 kg).
Am I also allowed to ride a motorcycle with category B?
No, category B licenses do not allow you to ride a motorcycle - you need a category A license to do so. However, Swiss car drivers no longer have to bother with driving lessons, theory test & etc., as they receive the additional category A1 after attending a 12-hour basic course. Category -A also requires a practical test.
How do you get an A1 driving license?
If you'd like to ride a small motorcycle, you have to be at least 15 years old for the A1 license. Anyone from age 16 can also ride larger motorcycles with the same driving license (see table). How much adults have to do for the A1 license depends on whether they already drive a car.
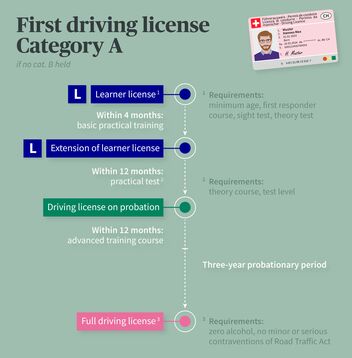
A1 driving license if no category B1/B held
- First responder course (max. 6 years old)
- Sight test (max. 24 months old)
- Theory test
- Learner license (4 + 12 months valid - extension after successfully completing basic practical training)
- Basic practical training (12 hours)
- Theory course (8 hours)
- Practical test
- After acquiring the driving license: advanced training course (7 hours)
Tip: as test dates are often quickly fully booked, it's best to apply for the advanced training course as soon as you've passed the driving test.
A1 driving license if category B1/B held
- Sight test (max. 24 months old)
- Learner license (valid for 4 months)
- Basic practical training (12 hours)
After you've successfully completed the basic practical training, you then receive the full A1 driving license without having to take a test. The probationary period lasts for three years.
What are the requirements for the A driving license?
If you'd like to ride larger motorcycles, you must be 18 years of age and initially apply for a category "A restricted" (-A) driving license. This is valid for motorcycles up to 48 PS and 35 kW engine output where the ratio of output to weight does not exceed 0.2 kW/kg. In a second step, you can apply for the "A unrestricted" (A) after you have ridden a restricted motorcycle for at least 2 years.
-A driving license if no category A1, B1 or B held
The process for getting the "A restricted" (-A) license is the same as A1 (see info graphics), but you also have to take a maneuvers test as part of the practical test.
-A driving license if category A1, B1 or B license held
The shorter route towards "A restricted" (-A) involves a few small steps. The differences with A1 are highlighted in bold.
- Sight test (max. 24 months old)
- Learner license (valid for 12 months)
- Basic practical training (12 hours)
- Practical test including maneuvers test
After passing the test, you receive the full "A restricted" (-A) driving license directly with no probationary period.
Two years' riding experience for "A unrestricted" (A)
After at least two years of unblemished riding (i.e. without having your license revoked) in the restricted category (-A), you can apply for the "A unrestricted" (A) license. To do so, you have to take another practical test (including a maneuvers test). If you pass this one, you can ride motorcycles without restriction from then on.
Winter break for practical tests
Road traffic offices do not normally carry out practical motorcycle license tests in the winter. This winter break or winter closure varies from canton to canton, but mainly lasts from November to March.
You must always take this into account in your plans so that you'll be able to take the test while your learner license is still valid. It cannot be extended during the winter break.
How much does a motorcycle license cost?
In Switzerland, you should expect a motorbike license to cost at least CHF 1,500. This amount represents fees and training course costs, but does not include motorcycle lessons. The prices vary enormously depending on canton of residence and region.
You can expect preparatory costs of around CHF 200 to 300. You need these things before you even ride your bike for the first time:
Preparatory costs
| To-do list in preparation for motorcycle license | Costs |
| Sight test | CHF 10 to 20 |
| First responder course | CHF 100 to 200 |
| Basic theory test | CHF 30 to 40 |
| 2 passport photos | CHF 10 |
| Learner license | CHF 40 to 80 |
You incur further costs while riding your motorcycle with a blue L plate. The cost of courses and tests amounts to some CHF 800 to 1,000 – excluding motorcycle lessons.
Costs in learning phase
| To-do list in learning phase for motorcycle license | Costs |
| Basic practical training | CHF 200 to 600 |
| Theory course | CHF 200 to 250 |
| Practical test | CHF 90 to 130 |
| Provisional driving license | CHF 30 to 70 |
| Possible motorcycle lessons | CHF to 120 per session |
Costs during the probationary period
You have to attend an advanced training course in the first 12 months of your three-year probationary period. This costs between CHF 300 and 500. After the probationary period, you pay a small fee for your full driving license to be automatically issued.
Costs for people with A1, B1 or B
If you already have an A1, B1 or B license, you can expect to pay between CHF 600 and 800 for a sight test, learner license, basic practical training and possibly a practical test.
If you subsequently upgrade to an "A unrestricted" (A) license, you have more costs, such as CHF 150 to 200 for your practical test and the issuing of the new driving license.
Do I have to have motorcycling lessons?
Motorcycling lessons are voluntary, but a very good idea. It's best not to try and save money here, as it's ultimately about your safety and that of other road users. Experience shows that some learners already feel very safe after just a few lessons, but it can take longer for others. Take the amount of time that you need.
What is the right motorcycle gear?
It’s worth investing in high-quality protective gear, as good protective clothing can help prevent serious injury in an accident - and ultimately save lives.
The following are part of the basic equipment:
- Helmet (compulsory): ideally an integral helmet with chin protector and visor.
- Combination: all-in-one suit or jacket and trousers. Protective fabric clothing is comfortable, water-repellent and slightly cheaper, but the best protection against abrasion is still leather. It's a good idea to have impact-reducing protectors for your back, shoulders, elbows, underarms and knees.
- Gloves: make sure you choose anti-abrasion material. If there's a collision, it's instinctive to fall, therefore a stable bar should protect your wrist.
- Boots: good motorcycle boots have a high, reinforced shaft, as the lower legs are at most risk in a fall.
Which types of insurance do you need for a motorcycle?
Motorcycle liability insurance
Liability insurance is compulsory in Switzerland for all motorcycles. The insurance covers injury to third parties. This means that if you cause an accident involving people, animals or property, the insurance will pay for the damage/injury, provided that you have obeyed the law.
Tip: you need a valid insurance certificate (liability insurance) to register your motorcycle and receive your number plates.
Partial or comprehensive accidental damage insurance
You can voluntarily take out accidental damage insurance for your motorcycle. The insurance covers damage to your own motorcycle.
- Partial accidental damage insurance covers damage to your motorcycle that was not caused by you (theft, natural hazards, vandalism etc.).
- Comprehensive accidental damage insurance covers damage to your motorcycle for which you were responsible, i.e. collision damage (e.g. when parking, maneuvering or in traffic).
Partial accidental damage insurance is relatively inexpensive and generally a good idea. Comprehensive accidental damage insurance is worth taking out for newer or very expensive machines.







