Charging electric cars – what you should look out for
Electromobility is steadily gaining popularity. Besides Tesla, BMW and Nissan, many other brands – including VW, Renault and Opel – have also launched electric cars. Over 203,000 of the almost 4.8 million cars currently registered in Switzerland are fully electric (as of 2024)– and this number is growing.
According to a study by Swiss eMobility, in 2035 over 2 million people in Switzerland will drive an electric car. Have you already made the switch, or are you thinking about doing it soon? Our facts about charging electric cars provide you with important information for making your decision.
Charging technology will be a vital factor in the success of electric cars.
Electric cars can drive without emissions, and due to their high level of efficiency and low operating costs, they also provide other incentives for drivers who are dissatisfied with combustion engines. However, its ultimate breakthrough on the market will depend heavily on how to charge electric cars, as charging with electricity still takes much longer.
Where can I charge my electric car?
Charging for electric cars can roughly be divided into two categories: Charging at home or at publicly available stations.
- Options for charging at home
At home, you can charge electric cars using a normal outlet or a special wall box. But it’s best not to use standard household sockets. At 2.3 kW, charging can take 15 hours or more. Moreover, the standard household socket is not designed to be used at full power over long periods.
If you want to be able to charge your car over longer periods at an available outside parking space or in your garage at home, you should invest in a wall box. This home charging station is either installed on the wall or freely as a pillar. Depending on the wall box and charging power, you can achieve up to 22 kW. This way, you can fully charge your car in just a few hours. For example, you can simply charge your car overnight and it will be ready to drive in the morning. You can also insure your home charging station as part of your electric car insurance. - Charging options at public charging stations
There are now charging stations at lots of locations throughout Switzerland, including rest stops, public parking lots, shopping malls and supermarkets. Companies are also starting to provide more charging stations for electric company cars or the electric cars of their employees. That promotes not only the company’s image, but often it can also be offset with government subsidies or tax advantages.
You can charge your car very quickly at fast charging stations. Here, the charging capacity is generally between 50 and 350 kW. However, the availability of fast charging stations is still limited and the costs of charging an electric car can also be comparatively high. Moreover, fast charging should not be an everyday solution, since it can lead to significant wear on the battery.
Did you know?
In Switzerland, there are already over 14,500 public charging stations, ten years prior there weren’t even 1,000 (as of 2024).
How long does it take to charge an electric car?
The charging time depends on the battery’s size, whether or not it’s completely empty, and its maximum charging capacity. The outside temperature and the model of car also play a part. Charging from a conventional household mains socket takes the longest, and you should only do this if you have no other option. A home charging station is quicker, while a fast charging station is the quickest option of all.
How to calculate the charging time:
What’s the fastest way to charge my electric car?
If you want enough charge for 200 km, and your car uses 20 kWh/100 km on average, you need 2 x 20 = 40 kWh.
Here’s how long it will take:
- At a wall box (11 kW charging capacity): 3 hours and 36 minutes
- At a fast charging station (50 kW charging capacity): 48 minutes
- At a fast charging station (100 kW charging capacity): 24 minutes
Differences between the various charging technologies: AC and DC charging
There are different types of charging technologies and they vary by feature and functionality. The two basic charging technologies are called AC and DC charging.
Standard household electricity is alternating current (AC). However, electric cars need direct current (DC). For this reason, the current has to be converted so that it can be used for electric vehicles.
At AC charging stations, the alternate current is converted directly in the car. DC charging stations complete this process prior to charging. That’s why the charging capacity of AC charging is usually lower than DC charging, and depending on the type of outlet, ranges between 2.3 and 22 kW. The advantage of AC charging is that the technology is cheaper. This remains standard for all typical wall boxes connected to a normal household. In the long term, slower AC charging is better for the battery because it places less stress on it.
Fast charging stations, in contrast, use DC charging. The charging capacity for this technology is significantly higher and can reach 50 kW or more. The advantage with DC charging is the significantly shorter charging time. For example, an average electric car can be charged from 0% to 80% within 30 minutes. However, a DC charging station is rarely installed for private use. It needs greater capacity, is more expensive and takes up more space. Overall, DC charging makes more sense for public charging stations, while a wall box for charging at home tends to use AC charging, which is slower but easier on the battery.
How much does it cost to charge at a public charging station?
The price at a public charging station may include a one-time charging fee, a price per kWh, and/or a parking fee. Prices can vary from charging station to charging station. As a rule, the faster the charging station, the more you have to pay. In other words, slower AC charging stations are cheaper.
Tips for charging electric cars efficiently
Here are some tips to help you charge your electric car more efficiently:
- Plan and optimize your charging time: It is advantageous to carefully plan your charging time. Ideally, you should charge your electric car when it is not needed, for example when you are working or at night.
- Charging and getting the most out of your battery life: Carefully charging the battery of your electric car will maximize its battery life. You should make sure that you don’t charge past or below a certain level. Charging between 20% and 80% of capacity is therefore recommended.
- Impact of the surrounding temperature on charging: The temperature of the battery has a big impact on charging efficiency. In the case of lower temperatures, the charging speed decreases and the capacity is reduced. To shorten charging time, you should try to charge your electric car in a garage.
- Use of regenerative energy: When you use regenerative energy sources like solar energy, you can reduce your charging costs and protect the environment. One option is to install solar panels on the roof of your home to charge your electric car with the energy they generate.
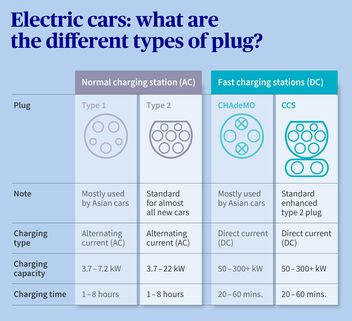
What types of plug are there, and what do I have to bear in mind when charging?
In Europe, there are typically two types of plugs: the type 2 plug (for AC charging) and the CCS plug (for DC charging). The type 2 plug is standard in Europe and is supported by almost all electric cars. The CCS plug is necessary if you want to use a fast charging station. In Asian car models, primarily CHAdeMO and type 1 plugs are used. A detailed overview of the various plug types is provided in the info graphic below.
Installing a charging station in a condominium
Do you own a condominium, and are you planning to buy an electric car? Then you should note the following points when installing a charging station:
- The meeting of condominium owners decides as to whether a charging station is to be installed, unless it’s going to be installed in a self-contained parking bay.
- You have to pay for an individual connection yourself. If the other owners aren’t prepared to share the basic installation cost, you have to pay that as well as the cost of the wall box for your personal parking space.
- If the owners want to ensure that more charging stations can be added in the future, you’ll need "smart" charging infrastructure. This involves a shared basic installation for the whole garage that the individual owners can have their personal wall box connected to as needed.
- In any case, it’s important to make sure that the electricity used can be billed separately. If multiple charging stations are in use in the same building, a smart power supply – also known as charging management or load management – can make sense.
- If the charging station is installed on the condominium property, future owners may be obligated to pay a share of the installation cost after the fact if they wish to use it.
Frequently asked questions about charging electric cars
How often should an electric car be charged?
An electric car can be charged as often as required. However, it is not recommended to regularly charge the battery to 100%. Instead, between 20% and 80% is advised to maximize the battery life of your vehicle.
Do I have to take my own charging cable with me to use public charging stations?
Usually, AC charging stations require you to bring your own charging cable, while DC fast charging stations often have a charging cable built in. Drivers of electric cars should always have a cable in their trunk to be on the safe side.
Can power outages occur if my electric car is charging at my home wall box?
There is a slight possibility that a power outage could occur if you are charging your electric car at your wall box. However, this depends on various factors, such as the capacity of your energy supply, the capacity of your wall box, the current, how long your charging time is, and the total load that is being used in your household at the same time.
Which home charging station is right for me?
Depending on your connection options, the number of cars you want to charge, the type of charging station, and how you want to be billed, there are various options for planning and installing a home charging station. For example, Swisscharge (in German) offers individual solutions for private use as well as charging infrastructure and load management for landlords and companies.
When is an electric car more sustainable than one with a gas or diesel engine?
This depends on a number of factors, including the amount of energy used to manufacture the car as well as the electricity needed to charge it. In Switzerland, approximately 70% of the electricity used through household sockets is from renewable energy sources. At many public charging stations, you can charge your vehicle up to 100% with certified green electricity. With Swisscharge (in German), for example, this is possible at the following charging stations:
- GOFAST
- Energie 360°
- IWB
- AGROLA
- Ewz







