
Nowadays, more and more employees from various sectors are suffering from occupational diseases. We show you how you can prevent this in your company and what you can do if your employees are affected.
Employees make the company – which is why health is also a top priority in the world of work. Take comprehensive precautions and provide your employees with a safe working environment to promote productivity and prevent occupational diseases.
Not all pain or illnesses that arise in direct connection with an occupation are considered an occupational disease. Which diseases can be included on the list of occupational diseases in Switzerland is defined in the Accident Insurance Act (UVG). According to this law, an illness must have been caused by the effects of certain work processes or harmful substances – and more than 50% of responsibility for the onset of the illness must be attributable to these factors. Illnesses that are not on the list of occupational diseases can only be recognized as occupational diseases if at least 75% of responsibility for the emergence of these illnesses can be assigned to the occupational activity.
As occupational diseases occur in every industry and in every profession, the list of occupational diseases is very comprehensive. However, the following occur especially often:
Note: These illnesses are only considered occupational diseases if they occur as a direct result of occupational activity. In the case of respiratory diseases, for example, this may be the case when working with flour dust in a bakery or in the case of skin diseases when working with chemical substances in a hairdressing salon.
Anyone who is exposed to harmful substances at work for many years, for example by handling building materials or aggressive cleaning agents, has a higher risk of developing an occupational disease. The substances that are considered harmful are set out in an extensive list in the Accident Insurance Ordinance (Appendix 1 UVV, in German).
Respiratory diseases are often caused by fine particle dust. A large amount of fine particle dust is produced during a wide variety of work, especially in manual trades. One of the most common occupational diseases caused by fine particle dust is pneumoconiosis. This exists in various forms and depends on the type of fine particles that are inhaled. For example, aluminosis is an occupational disease where the person has come into contact with aluminum.
Incidentally: Occupations in which there is high exposure to particulate matter are generally insured with SUVA.
However, occupational diseases can also be caused by other factors, such as UV radiation or noise. Heavy physical strain also plays a major role. For this reason, it is immensely important to protect yourself and your employees and to take suitable preventive measures in your company.
There are different tasks and work processes in every occupational field. You should therefore think about how you can offer your employees the best protection in all areas. In some cases, protective measures such as safety shoes or goggles are required by law. Health prevention measures at your company could look like this, for example:
These are just a few examples of how you can protect yourself and your employees against occupational diseases. Think about which prevention measures could still be relevant at your company and remind yourself of these regularly. Also inform your employees about all occupational risks, as you also benefit from their health. Healthy employees are demonstrably more productive and help you and your company to be successful.
It’s not always easy to recognize an occupational disease. Therefore, pay attention to changes in your employees and approach them openly.
If an employee is unable to work due to an occupational disease, they must consult a doctor and provide you with a medical certificate. This officially confirms the illness and the inability to work and is important for protection against dismissal and continued payment of wages.
If an occupational disease is actually present, you as the employer are obligated to notify the accident insurance immediately. This is your point of contact for both occupational diseases and accidents at work.
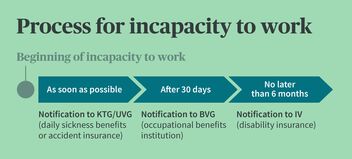
According to the Accident Insurance Act (UVG), an occupational disease in Switzerland is treated in the same way as an occupational accident. This means that benefits are also paid by the accident insurance provider. As an employer, you are legally obligated to insure your employees against occupational diseases and accidents.
If an occupational disease is actually attributable to harmful substances or certain activities, Suva can determine that a person is unfit for work. In this case, a change of occupation is unavoidable. In order to protect occupationally ill persons against financial losses, accident insurance generally covers certain transitional benefits for retraining or reorientation in addition to other social insurance.
It can also be difficult for you as an entrepreneur if employees are unable to work due to an occupational disease. After all, their expertise plays an important role in your company. For this reason, the focus should be on job retention and structured support and reintegration, where possible. For this, there are the following options:
AXA’s Care and Case Management offers professional support to ensure that the reintegration process runs smoothly.
The same conditions apply to occupational diseases as to non-occupational diseases: Employees enjoy protection against termination.
There are certain blocking periods after the end of the probationary period:
After these periods have expired or after employees have returned to work, the principle of freedom of termination applies. This means that both employers and employees can terminate the employment relationship.